psoas stretches pdf

The psoas muscle‚ a deep core muscle‚ plays a crucial role in hip flexion and posture. It connects the lower back to the femur‚ influencing movement and stability.
1.1 Understanding the Role of the Psoas in Movement
The psoas muscle‚ often referred to as the “king of muscles‚” plays a vital role in movement by acting as the body’s primary hip flexor. It is deeply embedded in the core‚ connecting the lower back to the femur‚ and is essential for activities like walking‚ running‚ and maintaining posture. The psoas facilitates hip flexion‚ enabling the leg to move toward the torso‚ which is crucial for locomotion. A healthy psoas allows for fluid‚ balanced movement‚ while tightness or imbalance can lead to discomfort or restricted mobility. Its function extends beyond movement‚ influencing overall stability and alignment‚ making it a cornerstone of muscular coordination and balance.
1.2 The Connection Between the Psoas and Low Back Pain
Tightness or imbalance in the psoas muscle is often linked to low back pain. The psoas originates in the lower back and inserts on the femur‚ meaning its tension can directly affect the lumbar spine. When the psoas is overactive or shortened‚ it can pull the spine out of alignment‚ leading to strain and discomfort. This tension is a common contributor to chronic low back pain‚ as it disrupts the body’s natural posture and movement patterns. Releasing and stretching the psoas can help alleviate this strain‚ promoting better spinal alignment and reducing pain in the lower back region.

Importance of Stretching the Psoas
Stretching the psoas enhances flexibility‚ improves posture‚ and reduces muscle tension‚ which can prevent pain and promote optimal movement. Regular stretching supports overall muscle balance and well-being.
2.1 Reducing Tension and Enhancing Flexibility
Stretching the psoas minimizes muscle tension and boosts flexibility‚ crucial for fluid movement. Tightness in this muscle can restrict hip mobility and posture‚ leading to discomfort or pain. By incorporating targeted stretches‚ individuals can release tension‚ allowing the thighs to lengthen and improve range of motion. This not only enhances physical comfort but also supports athletic performance and daily activities. Regular stretching helps maintain muscle balance‚ preventing imbalances that could cause injuries. Over time‚ consistent practice fosters a more relaxed and flexible psoas‚ contributing to overall musculoskeletal health and resilience.
2.2 Improving Posture and Reducing Lower Back Strain
Stretching the psoas muscle significantly improves posture by reducing unnecessary curvature of the lower back. A tight psoas can pull the pelvis out of alignment‚ straining the lumbar spine and leading to discomfort. By releasing tension in this muscle‚ the pelvis and spine can return to a more neutral position‚ alleviating lower back strain. Proper stretching helps distribute the workload of movement more evenly across the body‚ reducing the risk of overuse injuries. Better posture also enhances breathing and overall physical efficiency‚ making daily activities less strenuous and more comfortable. Regular psoas stretching is a simple yet effective way to support long-term spinal health and alignment.
Yoga Poses for Psoas Stretches
Yoga offers effective stretches for the psoas‚ such as Cobra Pose and Seated Forward Bend‚ which target the muscle to release tension and enhance flexibility naturally.
3.1 Cobra Pose (Bhujangasana)
Cobra Pose‚ or Bhujangasana‚ is a powerful yoga stretch that targets the psoas muscle. By lying on your stomach and lifting your chest‚ you engage the front body‚ stretching the hip flexors and lower back. This pose helps release tension in the psoas‚ promoting better flexibility and posture. It’s especially beneficial for those with tight hips or low back pain‚ as it gently lengthens the muscle without strain. To deepen the stretch‚ focus on lifting from the sternum rather than the head‚ ensuring a safe and effective release of the psoas. Regular practice can enhance movement and reduce discomfort.
3.2 Seated Forward Bend (Paschimottanasana)
Seated Forward Bend‚ or Paschimottanasana‚ is a yoga pose that deeply stretches the psoas muscle. Sit on the floor with legs extended‚ then fold forward from the hips‚ reaching for your toes. This stretch targets the entire back side of the body‚ including the hamstrings and spine‚ while gently releasing the psoas. To enhance the stretch‚ keep your back straight and engage your core. Holding this pose for several breaths can relieve lower back pain and improve flexibility. It’s a great way to release tension in the psoas without putting excessive strain on the body. Regular practice can lead to better posture and reduced muscle tightness.
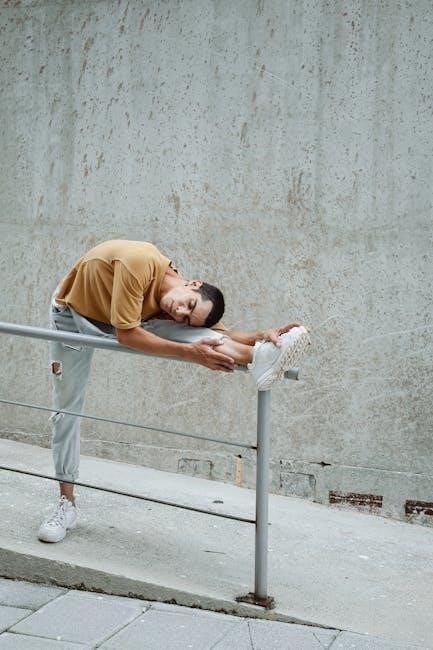

Prone Hip Flexor Stretches
Prone hip flexor stretches target the psoas and hip flexors. Lie on your stomach‚ lift one leg‚ and hold. Use a table or bed for support. Keep the opposite hip stable for effective stretching.
4.1 Prone Hip Flexor Table Stretch
Begin by lying on a sturdy table or high bed with one leg hanging freely off the edge. Ensure the leg remains straight to target the hip flexors effectively. Prop yourself up on your hands for stability and control. Slowly lift the hanging leg‚ keeping it straight‚ and hold for 20-30 seconds. This stretch helps release tension in the psoas and hip flexors‚ improving flexibility and reducing discomfort; Repeat on the other side for balanced benefits. Proper alignment and gentle movement are key to maximizing the stretch without causing strain.
4.2 Knee-to-Ankle Stretch Variation
Lie on a table or bed with one leg hanging off the edge. Bend the knee of the hanging leg‚ bringing the heel toward the opposite ankle. Gently push the knee downward until a stretch is felt in the hip flexor. Hold for 20-30 seconds‚ ensuring controlled movement to avoid strain. This variation targets the psoas and hip flexors‚ promoting flexibility and relief from tension. Perform on both sides for balanced results. Proper alignment and gradual stretching are essential for effectiveness and safety.

Seated Psoas Stretches
Seated psoas stretches effectively target the muscle while improving posture and reducing lower back strain. They enhance flexibility and promote proper alignment for optimal results.
5.1 Seated Psoas Stretch
Sit on a chair with feet flat on the floor‚ hands behind hips for support. Slowly tilt pelvis back‚ arching the lower back gently. Inhale deeply‚ then exhale while leaning slightly backward‚ stretching the front of the hips. Keep the opposite hip pressed into the seat and maintain a straight back. Hold the stretch for 20-30 seconds‚ breathing naturally. This stretch targets the psoas‚ relieving tension and enhancing flexibility. Regular practice can improve posture and reduce lower back strain‚ promoting overall hip mobility and comfort.
5.2 Seated Forward Bend with Psoas Focus
Sit on the floor with legs extended straight‚ feet flexed. Inhale deeply‚ lengthening the spine. Exhale slowly‚ folding forward from the hips‚ reaching for shins or toes. Keep knees slightly bent if necessary. Focus on stretching the front of the hips and lower back‚ engaging the psoas. Hold for 30 seconds‚ breathing deeply. This stretch enhances flexibility‚ reduces tension‚ and improves posture; Regular practice can alleviate lower back strain and promote better hip mobility. Ensure proper alignment to avoid discomfort and maximize the stretch’s benefits. This pose complements other psoas stretches‚ offering a holistic approach to muscle relief and overall well-being.

Releasing the Psoas with Tools
Use tools like a kettlebell‚ roller‚ or ball to gently release the psoas. Apply pressure and roll slowly‚ focusing on the lower abdomen and hip area.
6.1 Using a Kettlebell or Roller for Release
A kettlebell or roller can effectively release psoas tension. Lie on your back‚ place the tool under your lower abdomen‚ and gently roll it back and forth. This helps relax the muscle‚ improving flexibility and reducing discomfort. Focus on slow‚ controlled movements to target the deep tissue without causing strain. Regular use can enhance posture and alleviate lower back pain‚ promoting overall mobility and relaxation. This method is particularly beneficial for those with tight hip flexors or chronic stiffness in the lumbar region. Consistency is key for long-term benefits.

Step-by-Step Guide to Psoas Stretching
A step-by-step guide ensures proper preparation‚ technique‚ and progression. Focus on controlled movements to enhance flexibility and reduce lower back strain effectively and safely always.
7.1 Preparing for Stretches
Preparing for psoas stretches involves creating a calm environment and warming up with light cardio. Lie on a firm surface with knees slightly bent to relax the lower back. Engage your core gently to stabilize the pelvis. Ensure your breath is deep and steady to maintain relaxation. Positioning is key; align your body properly to target the psoas effectively. Avoid forcing stretches‚ as this can cause strain. Start slowly‚ focusing on controlled movements to enhance flexibility and release tension without discomfort. Proper preparation ensures a safe and effective stretching routine for the psoas muscle.